Analysis of document images
2020-2022 : This research project aims to explore the multimodal text-visual feature representations to detect the types of documents by classifying the input document images. The chanllenge for text-visual multimodal learning is to learn a common representation space from the heterogeneous features extracted from the language and visual model respectively. Different multimodal methods such as Vanille Multimodal feature fusion, Mutual learning based on Knowledge Distillation, Cross self-attention between text and visual modality are applied in this research.
- Collabration labotories: L3i, CVC
- with Souhail Bakkali, Mickaël Coustaty, Marçal Rusiñol, Oriol Ramos Terrades
Reasearch methods:
Key words: cross-modal representation, text-visual cross self-attention, Self-supervised contrastive learning, BERT, CNNs, document image classification
In this work we approach the document classification problem by learning cross-modal representations through language and vision cues, considering intra- and inter-modality relationships. Instead of merging features from different modalities into a common representations space, the proposed method exploits high-level interactions and learns semantic information from effective attention flows within and across modalities. The proposed learning objective enforces the compactness of intra-class representations while separating inter-class features by contrasting positive and negative sample pairs within and across each modality. Unlike the classic uni-modal contrastive learning, we propose cross-modal contrastive learning loss to further explore the relations between vision and text cues. Extensive experiments on public document classification datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and the generalization capacity of our method on low-scale and large-scale datasets, by including cross-modal pre-training in a unified network..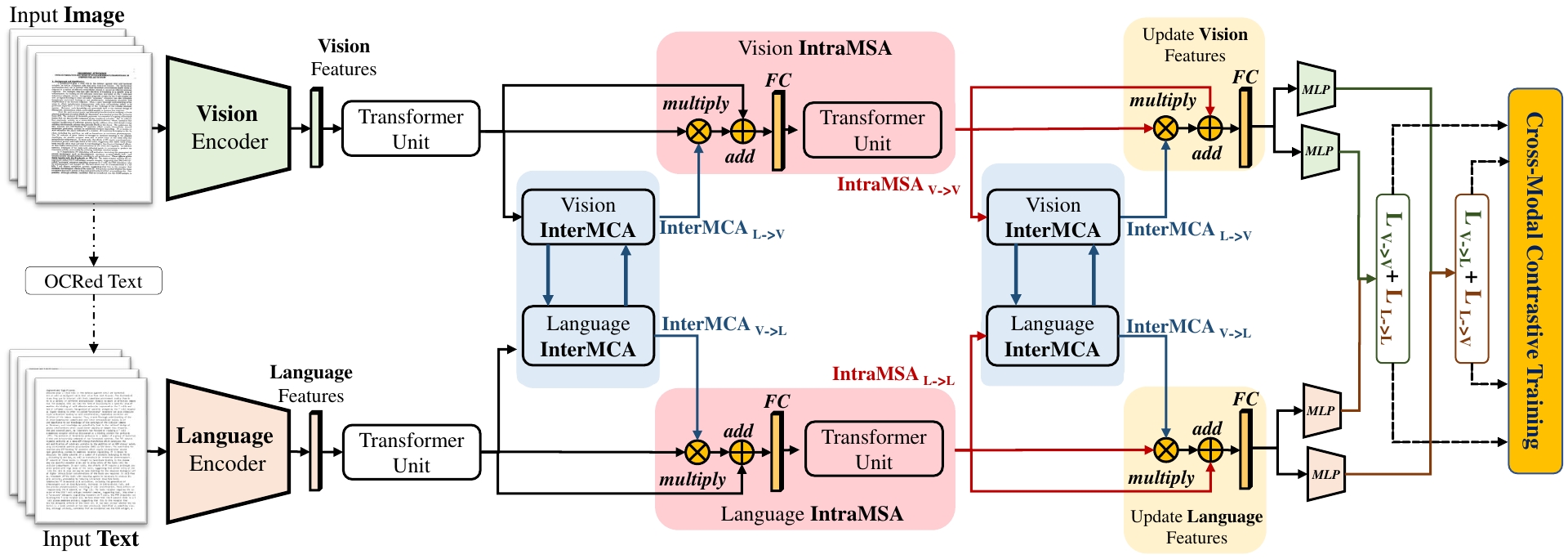
Key words: Text document image classification, Self-attention-based fusion, Mutual learning, Multi-modal fusion Ensemble learning
The main challenge of document image classification is the low inter-class discrimination and high intra-class structural variations of document images. To mitigate this issue, we propose a mutual learning module that serves as a block in our ensemble trainable network which allows the network to simultaneously learn the discriminant features of image and text branches in a mutual learning manner. Specifically, we design a novel mutual learning model, namely positive mutual learning, which enables the current branch to learn the positive knowledge from the other branch instead of the negative knowledge that will weaken the learning capacity for the current branch. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time to leverage (positive) mutual learning approach for document image classification. The experimental results show the effectiveness of our approach which improves the classification performance of document images for the independent branches.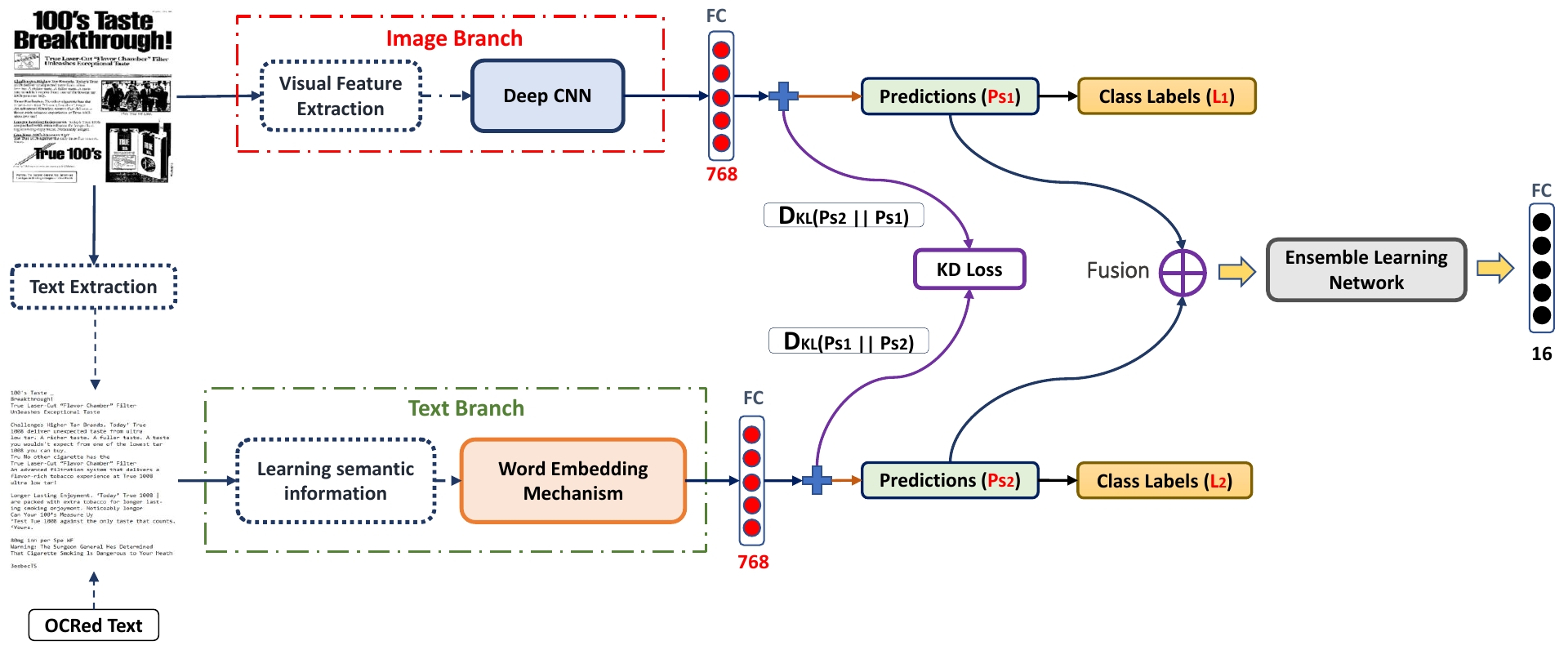
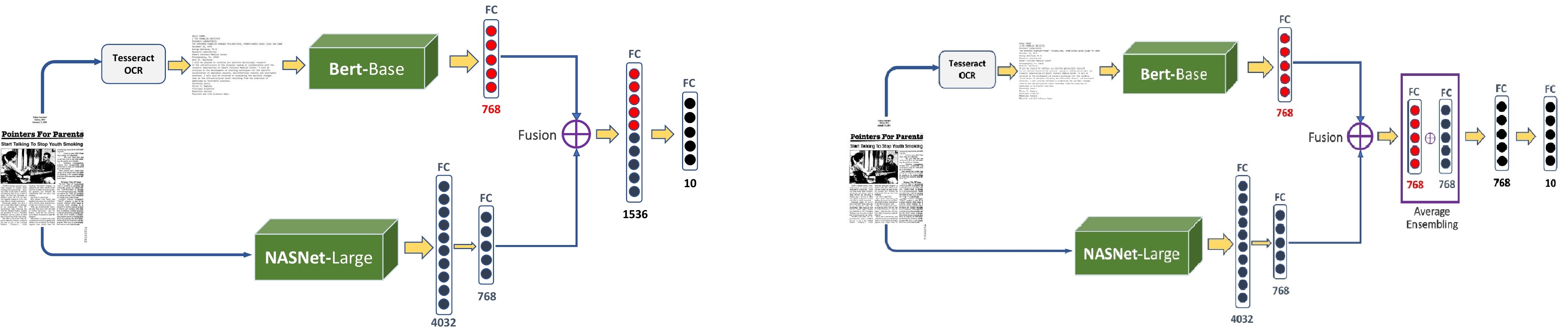
Key words: Text document image classification, cross-modal feature learning, deep CNNs.
Unlike the general image classification problem in the computer vision field, text document images contain both the visual cues and the corresponding text within the image. However, how to bridge these two different modalities and leverage textual and visual features to classify text document images remains challenging. In this paper, we present a two-branches based cross-modal deep network that enables to capture both the textual content and the visual information. We conduct an exhaustive investigation of nowadays widely used neural networks such as ResNet, MobileNet, NASNet-Large, Bert and so on as backbone to extract image and text features respectively. Different joint feature learning approaches based on vanille concatenation, equal concatenation and superposition have been introduced to learn the common multimodal features from the language and visual cues.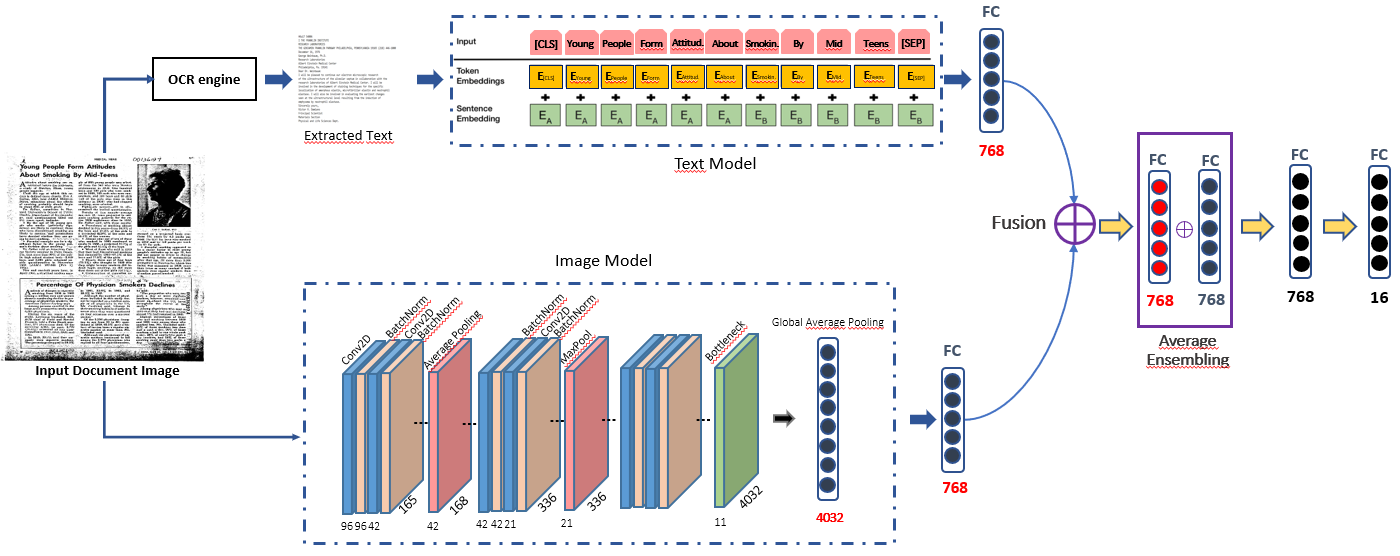
Document attributes classification
Exploring Multi-Tasking Learning in Document Attribute Classification [Pattern Recognition Letters] [code]:
- Collabration labotories: IMT Atlantique, Thapar University
- with Tanmoy Mondal, Abhijit Das
Key words: Document attributes classification, multi-task learning, hybrid CNNs.
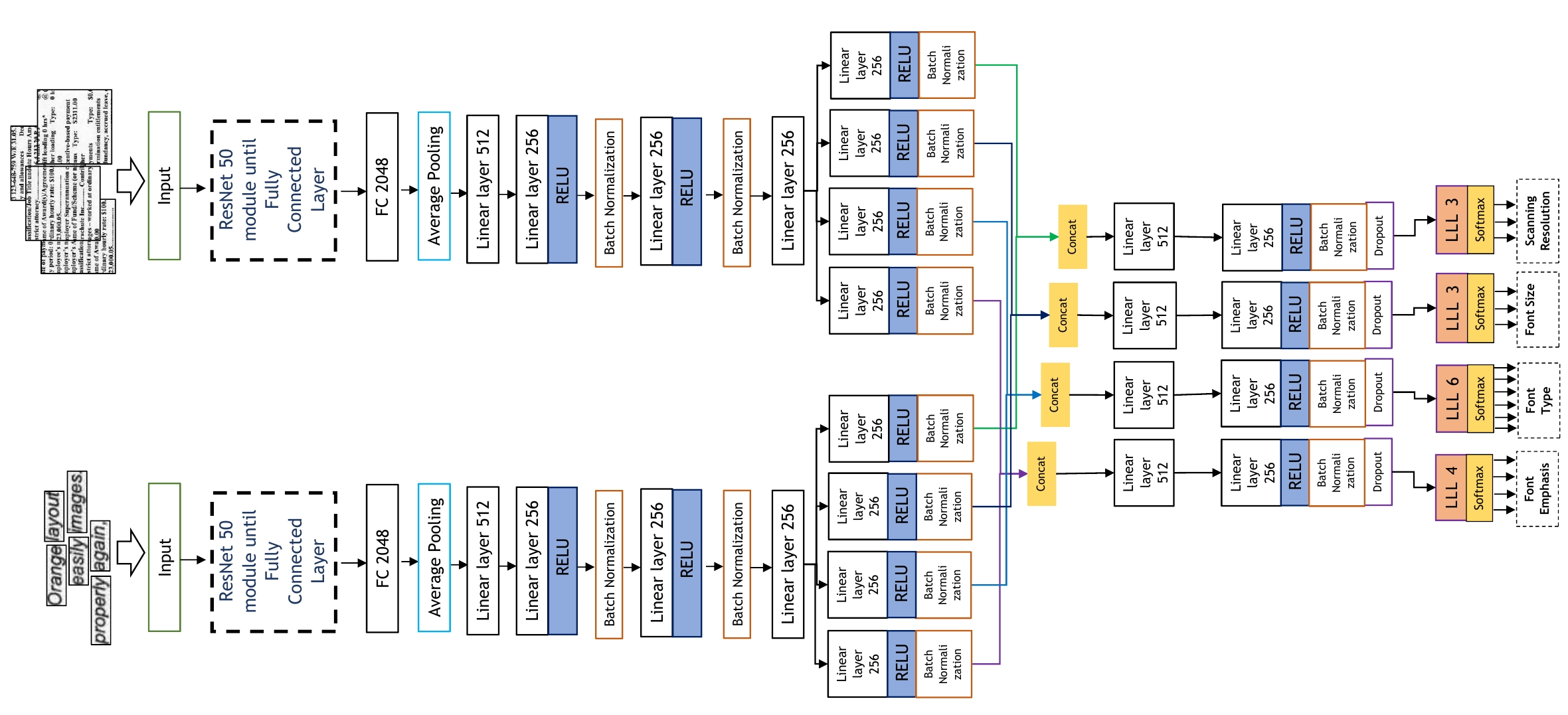
In this work, we adhere to explore a Multi-Tasking learning (MTL) based network to perform document attribute classification such as the font type, font size, font emphasis and scanning resolution classification of a document image. To accomplish these tasks, we operate on either segmented word level or on uniformed size patches randomly cropped out of the document. Furthermore, a hybrid convolution neural network (CNN) architecture "MTL+MI", which is based on the combination of MTL and Multi-Instance (MI) of patch and word is used to accomplish joint learning for the classification of the same document attributes.