IDECYS+ : la détection de l'usurpation d'identité (FUI 25)
2020-2022 : The IDECYS+ project aims to develop a new flexible and secure digital identity solution for facial anti-spoofing for European legal entities, and primarily for the 3 million French TPE/PME. This project proposed a solution based on deep learning to distinguish facial attacks by printed photo, video or 3D mask by integrating into the facial identification system:
- Collabration labotories: L3i, AriadNext
- with Jean-Christophe Burie, Muriel Visani, Petra Gomez-Krämer, Muhammad Muzzamil LUQMAN, Marchand Sylvain, Ahmad Montaser Awal
Reasearch methods: The challenge of face anti-spoofing is to distinguish the real presentation from the presentation attacks with fine difference in terms of image texture. The methods based on long/short-term attention for fine-grained classification, multimodal learning, multitask learning are proposed for FAS in this project.
Key words: Video-based transformer, multi-scale multi-head self-attention, face presentation attack detection
Many works based on Convolution Neural Networks (CNNs) for face PAD formulate the problem as an image-level binary classification task without considering the context. Alternatively, Vision Transformers (ViT) using self-attention to attend the context of an image become the mainstreams in face PAD. Inspired by ViT, we design a Video-based Transformer for face PAD with short/long-range spatio-temporal attention which can not only focus on local details but also the context of a video. The proposed Multi-scale Multi-Head Self-Attention enables the model to learn a fine-grained representation to perform pixel level discrimination required by face PAD. We also introduce convolutions to our ViTransPAD to integrate desirable proprieties of CNNs which can gain a good computation-accuracy balance. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach using video-based transformer for face PAD which can serve as a new backbone for further study.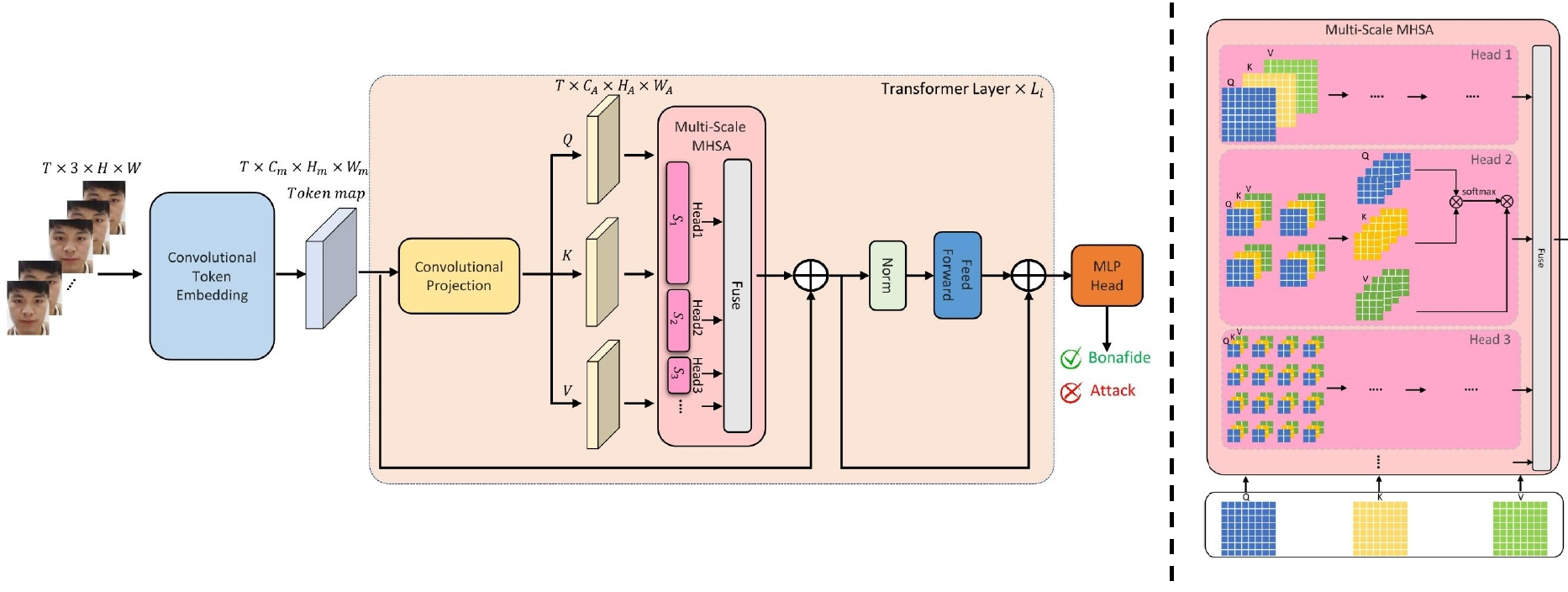
Key words: Multimodal learning, 3D depth image generalization, CNNs, face presentation attack detection
Since the real faces and the attacks presented in such as 3D depth images, infrared images or thermal images are very different as shown in WMCA, using multimodal learning for face anti-spoofing is a effective way. However, acquiring the images of special modality needs special sensors which is not practical for the current consuming devices. Thus, we propose a method based on CNNs-based encoder-decoder architecture which allows to generate the pseudo multimodal images (e.g., 3D depth image) to detetect by multimodal learning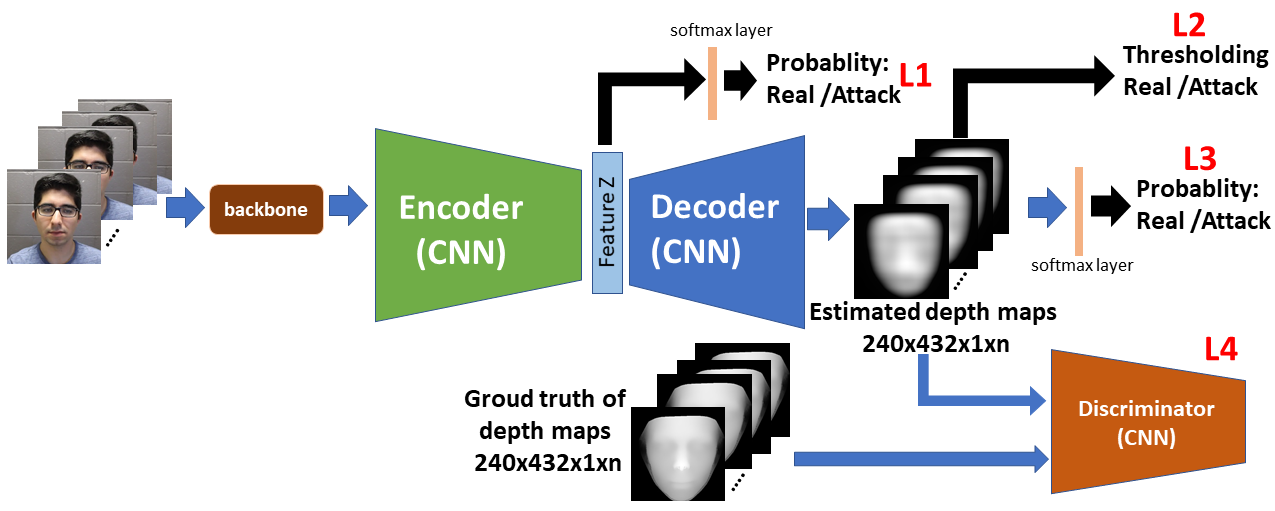
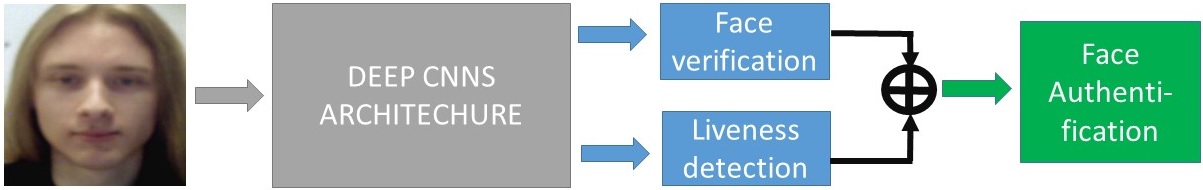
Key words: Multi-task learning, interactive face authentification, face recognition, facial expression recognition, CNNs
Existing face verification architectures seldom integrate any liveness detection or keep such stage isolated from face verification as if it was irrelevant. This may potentially result in the system being exposed to spoof attacks between the two stages. This work introduces FaceLiveNet, a holistic endto-end deep networks which can perform face verification and liveness detection simultaneously. An interactive scheme for facial expression recognition is proposed to perform liveness detection, providing better generalization capacity and higher security level. The proposed framework is low-cost as it relies on commodity hardware instead of costly sensors, and lightweight with much fewer parameters comparing to the other popular deep networks such as VGG16 and FaceNet. Experimental results on the benchmarks LFW, YTF, CK+, OuluCASIA, SFEW, FER2013 demonstrate that the proposed FaceLiveNet can achieve state-of art performance or better for both face verification and facial expression recognition. We also introduce a new protocol to evaluate the global performance for face authentication with the fusion of face verification and interactive facial expression-based liveness detection.